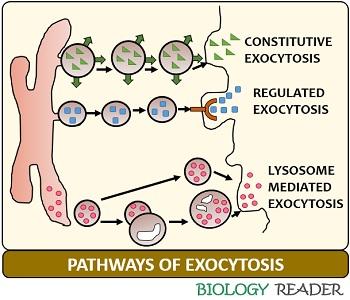
Constructive exocytosis is the ordinary exocytotic mechanism that occurs in four steps, whereas regulatory exocytosis occurs in five steps The steps are as follows Vesicle trafficking – Motor proteins such as kinesins, dyneins, and myosins assist in the transport of cell vesicles to the cell membrane via the cytoskeleton's microtubules Below is an outline of the basic steps of exocytosis A vesicle is formed, typically within the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus or early endosomes The vesicle travels to the cell membraneEndocytosis Vs Exocytosis Definitions, Types of Exocytosis Exocytosis Definition Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis is describing transport Exocytosis is a type of active transport through which materials are transported and released into the extracellular environment (or transported to the plasma membrane)Here, materials (waste products, recycled materials, or important substances
What Is Exocytosis Definition Pathways Steps Example Biology Reader
Exocytosis process steps
Exocytosis process steps-Answer to Describe the process of exocytosis using the example of a nerve synapse By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutionsThe material to be exported is filtered through the Golgi apparatus, which forms vesicles and steps towards the plasma membrane These packets then fuse with the membrane and are finally thrown out of the cell Some hormones and numerous digestive enzymes follow the exocytosis process to get out of the cell




Steps In Neuronal Exocytosis Synaptic Vesicles Containing Download Scientific Diagram
Gravity Endocytosis Step 1 Click card to see definition 👆 Tap card to see definition 👆 The cell comes into contact with a particle Click again to see term 👆 Tap again to see term 👆 Endocytosis Step 2 Step 1 Vesicle Trafficking The first step of exocytosis during which the secretory vesicle move from their spot of creation to the cell membrane This is an energyconsuming step Step 2 Vesicle Tethering On reaching the cell membrane, the outgoing vesicle becomes linked to, and is pulled into close contact with the cell membrane Exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their contents to the outside of the cell, as shown in the Figure below Exocytosis occurs when a cell produces substances for export, such as a protein, or when the cell is getting rid of a waste product or a toxin
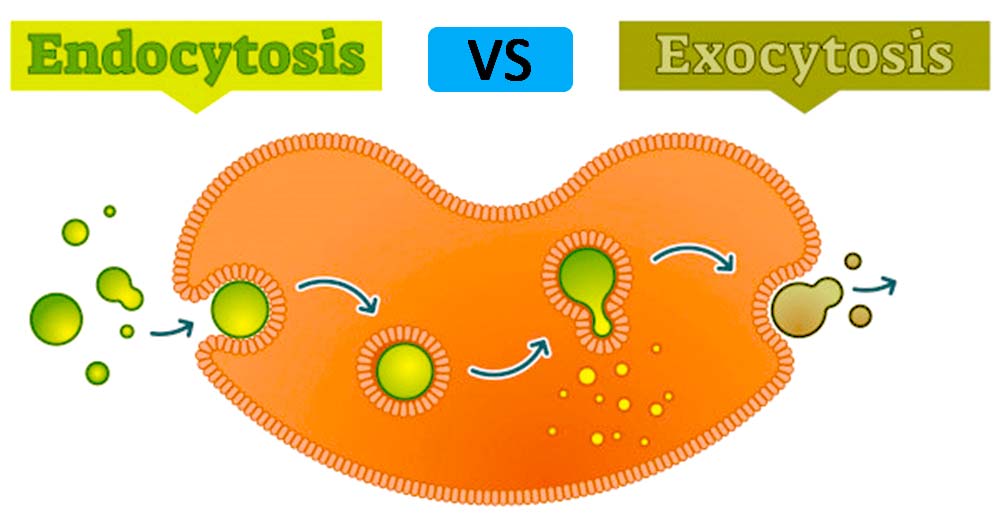
Exocytosis is a general term used to denote vesicle fusion at the plasma membrane, and it is the final step in the secretory pathway that typically begins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), passes through the Golgi apparatus, and ends at the outside of the cell Endocytosis refers to the recovery of vesicles from the plasma membrane Exocytosis Stages Although the process of moving a complex molecule across the microscopic distance from an organelle to the cell membrane seems simple, there are a few distinct stages that make this movement possible Vesicle Trafficking The fusion process is triggered by Ca 2 influx and requires the participation of Ca 2 sensors In addition to triggering the final fusion, Ca 2 signal is also involved in the steps prior to fusion, indicating that Ca 2binding proteins potentially contribute to earlier stages of vesicle exocytosis (Regehr, 12)
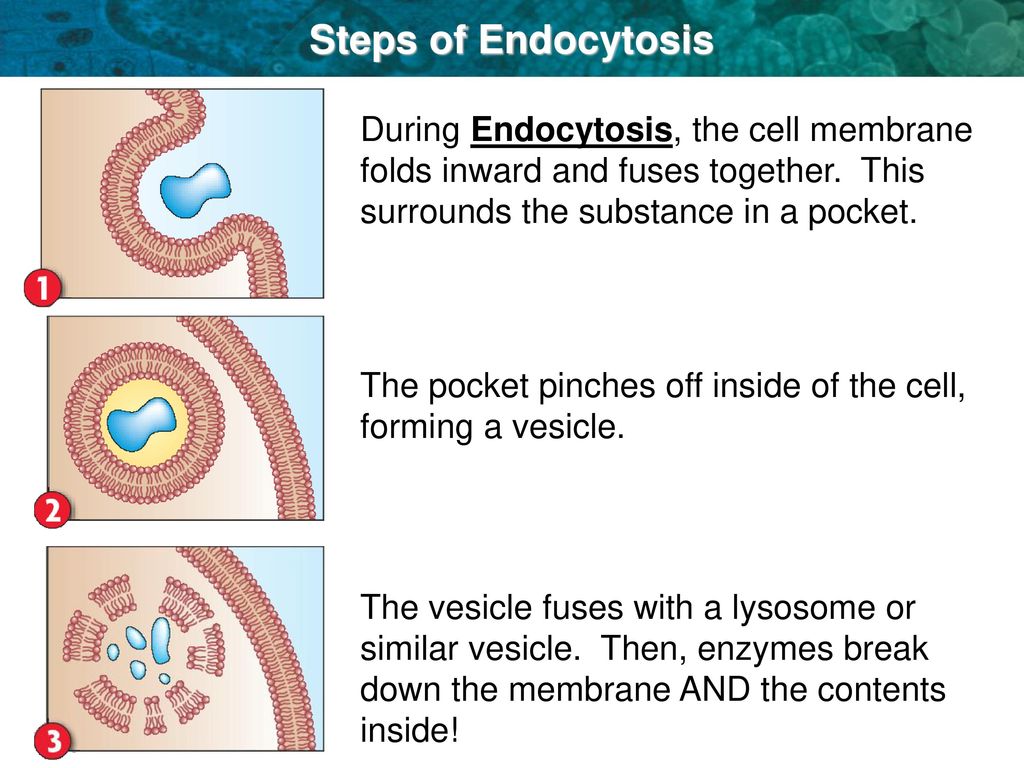
Docking – This is the attachment of the vesicles with the cell membrane, initiating the merging of the phospholipids of the vesicle membrane with that of the cell membrane Priming – This step takes place in the regulated exocytosis and not in the constitutive exocytosis The cell membrane curves to the inside of the cell as the cytoplasm underneath becomes more soluble This cell membrane surrounds the particle to be engulfed A vesicle is formed by the en around this particle This vesicle pinches off to the cytoplasm inside the cellNeural Communication The nervous system is the principal regulatory system in animals, which is required to survive and maintain homeostasis The nervous system along with the endocrine system jointly coordinate and integrate all the activities of the organs and regulate physiological processes so that they function in a synchronised manner




3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Key



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis
Exocytosis {Exo (exit) cytosis (cell)} The process by which large amounts of material, or large nondissolved particles, are moved from the cell's cytoplasm to the outside environment 6 hoW does endocytosis Work? the steps of exocytosis is the process by which a substance is released from the cell through a vesicle that transports the substance to the cell surface and then fuses with the membrane to let Step 6 Elimination or exocytosis The digested contents of the phagolysosome are then eliminated in a process called exocytosis References and further readings Punt, Jenni, Stranford, Sharon, Jones, Patricia, & Owen, Judy (18) Kuby Immunology (Eighth edition) W H Freeman The Innate Immune System Phagocytosis—The Process of




Endocytosis Definition Process And Types With Examples



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy
The steps of exocytosis (Figure 16) are as follows The vesicles that transport particles from Golgi apparatus to the cell membrane are recycled to transport new particles (step 1; There are up to five main steps to exocytosis (constitutive exocytosis uses four steps, regulative exocytosis uses five steps) Trafficking ; Endocytosis works in three basic steps The cell membrane folds inward, forming a cavity that contains fluid, dissolved substances, food materials, foreign matter, microorganisms, and some other substances This process is known as invagination




Calcium Independent Exo Endocytosis Coupling At Small Central Synapses Sciencedirect




Regulated And Constitutive Exocytosis Of Cytokines Representative Download Scientific Diagram
It is when cellular waste products travel in vesicles to the surface of the cell membrane and are released, thereby exiting the cell Several complex molecular mechanisms are implicated in vesicle exocytosis In general, the process occurs in three main steps vesicle docking, priming, and fusion 11Introduction to exocytosis!Watch the next lesson https//wwwkhanacademyorg/science/biology/energyandenzymes/energyinmetabolism/v/introductiontometab




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I




Exocytosis Wikipedia
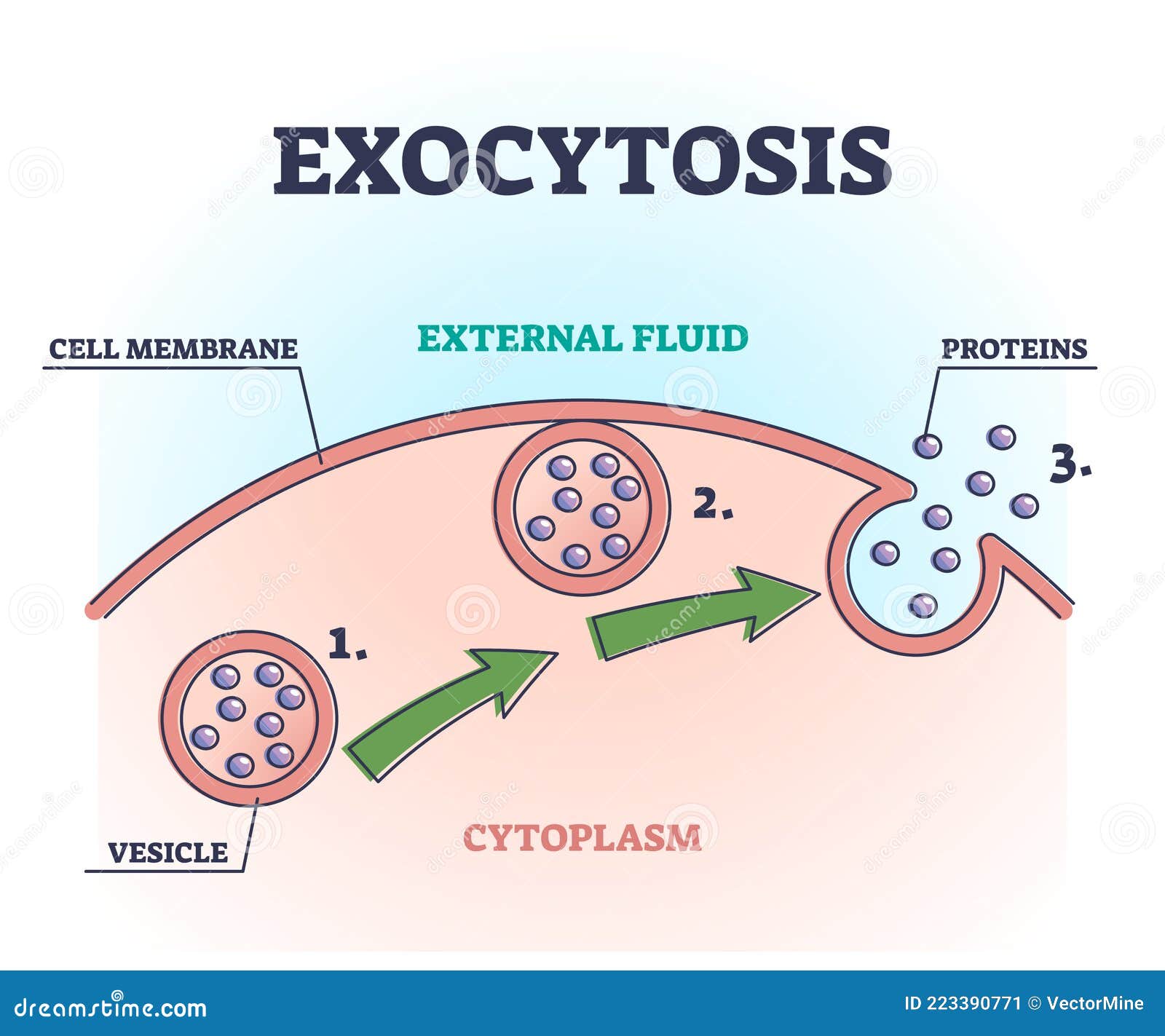
Steps of exocytosis include vesicle trafficking, tethering, docking, priming, and fusing Vesicle fusion with the cell membrane may be complete or temporary Exocytosis occurs in many cells including pancreatic cells and neuronsExocytosis a process in which material inside a cell is packaged into vesicles and excreted into the extracellular medium Endocytosis a process in which the plasma membrane invaginates or fold inward, to form a vesicle that brings substances into the cell Definition 3 3 ExocytosisExocytosis is defined as the transport and fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane and the extracellular space There are three exocytosis pathways that deliver vesicles to the plasma membrane Found in all cells, the constitutive secretory pathway operates continuously to deliver freshly synthesized membrane lipids and proteins, and soluble




Reciprocal Link Between Cell Biomechanics And Exocytosis Wang 18 Traffic Wiley Online Library




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks
Steps of exocytosis include vesicle trafficking, tethering, docking, priming, and fusing Vesicle fusion with the cell membrane may be complete or temporary Exocytosis occurs in many cells including pancreatic cells and neuronsThis process also involves formation of a vacuole or vesicle around the molecule as it is completely ingested Step 4 Digestion In some cells, enzymes in the vesicle (eg lysosome) break down the molecule into simpler components Waste materials that cannot be used are then removed from the cell through a process known as exocytosis In order to maintain cell size, membrane components must be replaced This is accomplished by the process of exocytosis Opposite to endocytosis, exocytosis involves the formation, transportation, and fusion of internal vesicles with the cell membrane to expel substances from the cell




Exocytosis Examples Triggers What Is Exocytosis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Exocytosis Springerlink
Exocytosis is the last step of the secretory pathway and it involves the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane, a process that, in fungi, ensures the delivery of cell wallsynthesizing enzymes, membrane proteins, and lipids in areas of active growth Endocytosis Definition Endocytosis is the process of actively transporting molecules into the cell by engulfing it with its membrane Endocytosis and exocytosis are used by all cells to transport molecules that cannot pass through the membrane passively Exocytosis provides the opposite function and pushes molecules out of the cellExocytosis is the opposite of the processes discussed in the last section in that its purpose is to expel material from the cell into the extracellular fluid Waste material is enveloped in a membrane and fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane This fusion opens the membranous envelope on the exterior of the cell, and the waste material
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_2-5ae36dab04d1cf003cef3c48.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples




Steps In Neuronal Exocytosis Synaptic Vesicles Containing Download Scientific Diagram
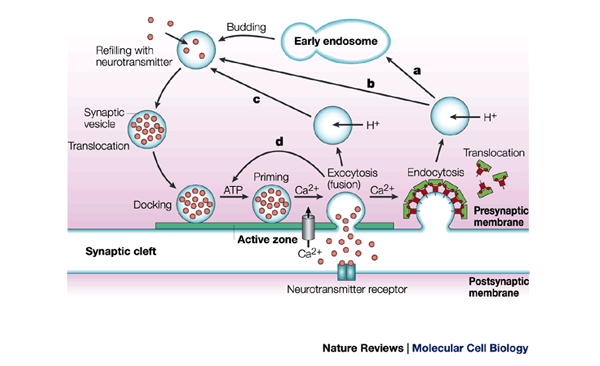
Regulated exocytosis is most often identified as the late step of protein and neurotransmitter secretion, consisting in the fusion between the membrane of secretory granule/ vesicle and the plasma membrane However, a large number of nonsecretory processes, often playing key roles in cellular function, are also based on regulated exocytosisView EXOCYTOSISdocx from SCI 003 at Technological Institute of the Philippines EXOCYTOSIS Exocytosis is the process of moving materials from within a cell to the exterior of the cell This processExocytosis The reverse process of moving material into a cell is the process of exocytosis Exocytosis is the opposite of the processes discussed in the last section in that its purpose is to expel material from the cell into the extracellular fluid Waste material is enveloped in a membrane and fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane
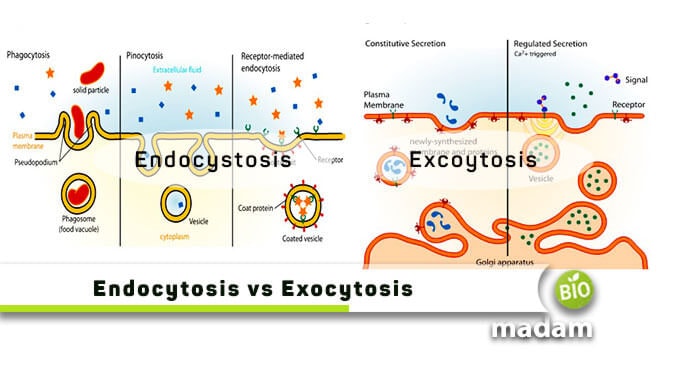



Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biomadam




Exocytosis By Vesicle Crumpling Maintains Apical Membrane Homeostasis During Exocrine Secretion Sciencedirect
7 Endocytosis is the case when a molecule causes the cell membrane to bulge inward, forming a vesicle Step 6 Cellular waste, such as broken down molecules that the cell cannot reuse, is discharged from the cell by the process of exocytosis Exocytosis is the opposite of endocytosis;Steps of Exocytosis Generally, exocytosis involves five steps for the expulsion of intracellular substances Vesicle trafficking In this step, the transportation of vesicles to the cell membrane occurs along with the microtubules of the cytoskeleton
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endocytosis-5ad64d57c0647100386364bb.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples
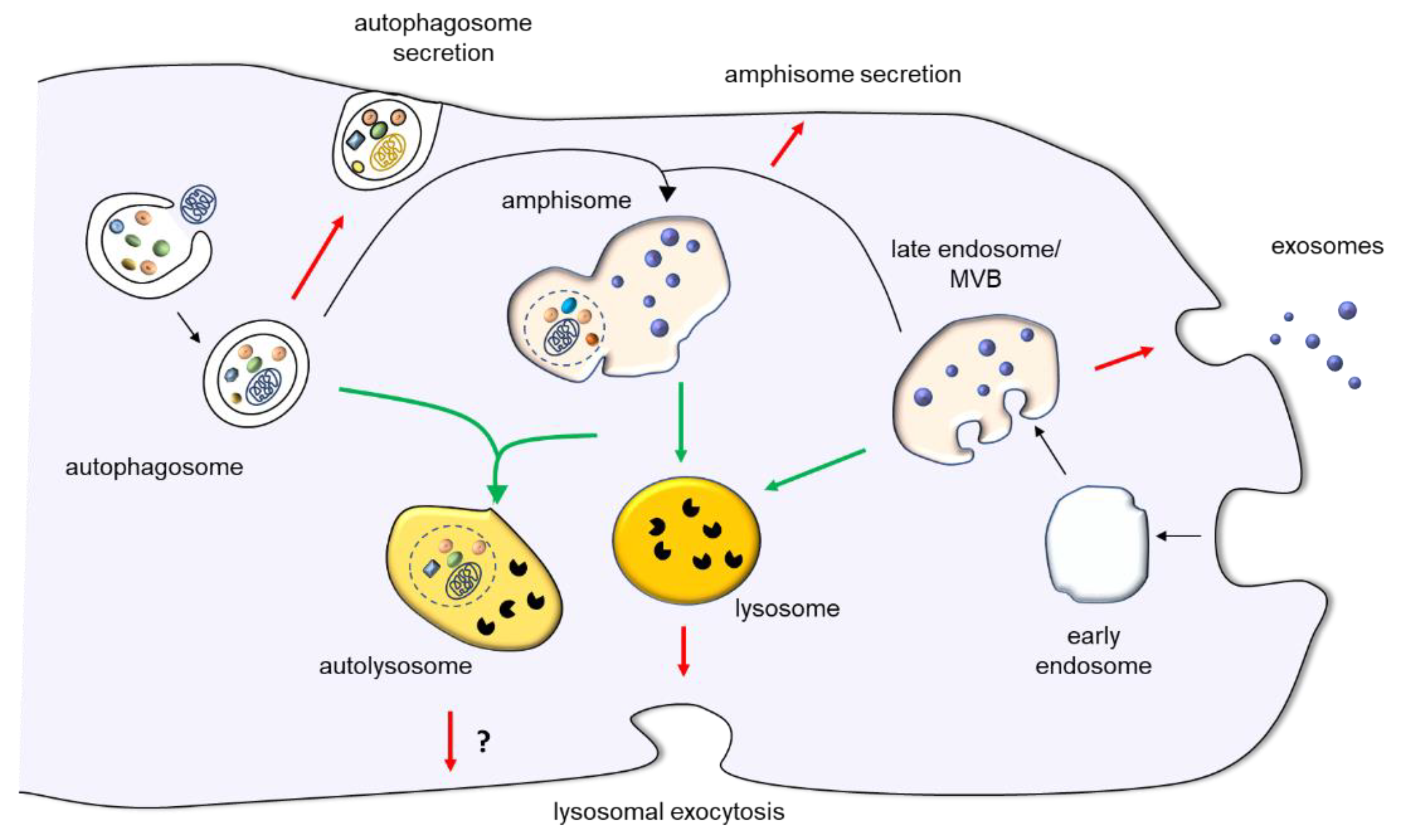



Ijms Free Full Text Lysosomal Exocytosis Exosome Release And Secretory Autophagy The Autophagic And Endo Lysosomal Systems Go Extracellular Html
Steps of exocytosis include vesicle trafficking, tethering, docking, priming, and fusing Vesicle fusion with the cell membrane may be complete or temporary Exocytosis occurs in many cells including pancreatic cells and neurons Complete info about it can be read here Then, what is the process of exocytosis?Nichols et al, 01) The vesicles containing nanoparticles are tethered or docked to the cell membrane (stepsExocytosis is the process of expelling substances from cells through the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane It is the counterpart to endocytosis
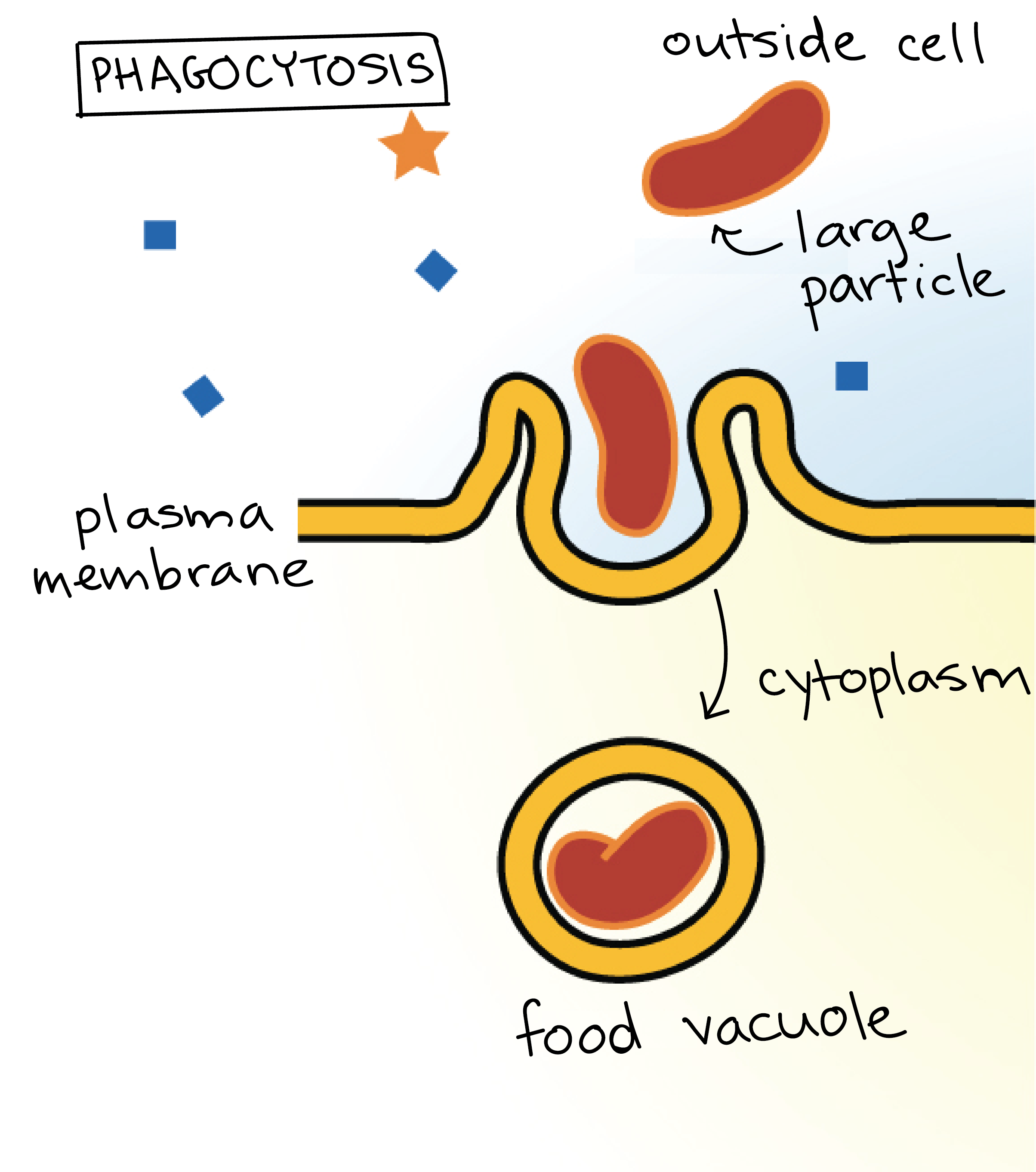



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy




Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The vesicle containing the material pushes it out through the membrane A vesicle is like a bubble that forms around material The vesicle has a coating that tells it where to go, and on this particular vesicle the coating says "Go to the membrane" The coating will then fuse to the membrane and push the material out of the cellExocytosis is relatively simple First you need something to release Let us take protein for example After it has been packaged and modified by the Golfing Apparatus from the cis side to the trans side, a vesicle around the protein is formed as Basic Process of Exocytosis Vesicles containing molecules are transported from within the cell to the cell membrane The vesicle membrane attaches to the cell membrane Fusion of the vesicle membrane with the cell membrane releases the vesicle contents outside the cell




Exocytosis Endocytosis Receptor Mediated Endocytosis Ppt Download
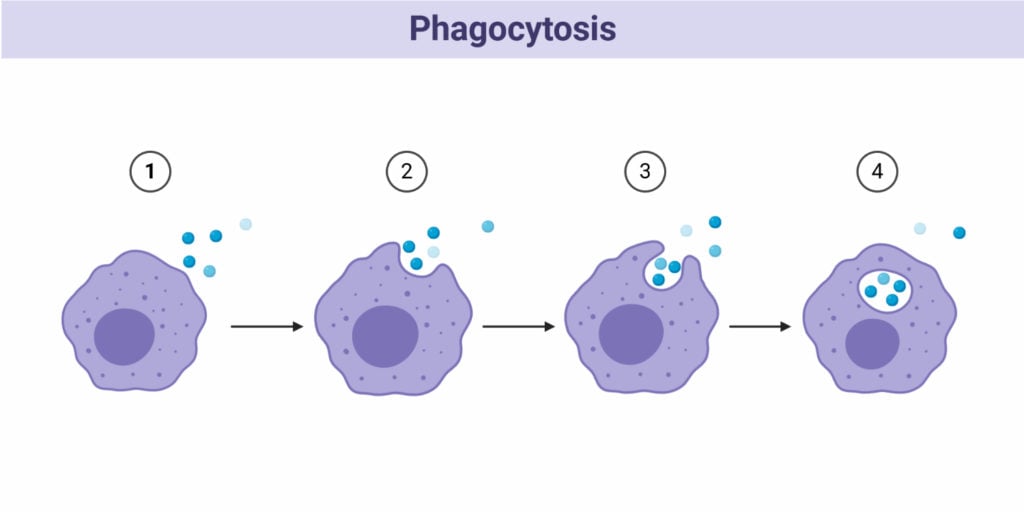



Endocytosis Definition Process And Types With Examples
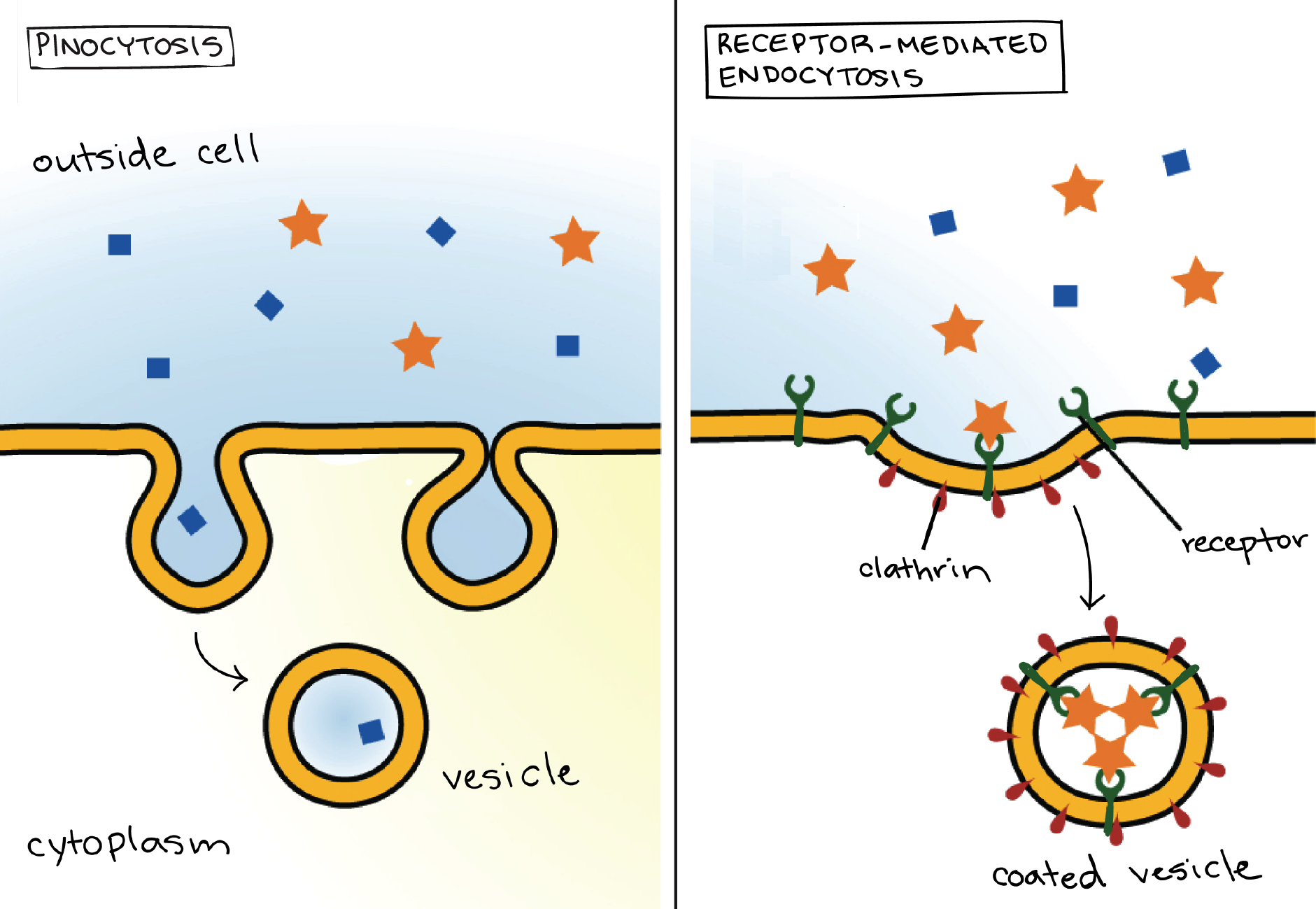
The process of Receptormediated endocytosis has the following steps The particles (ligands) that need to be synthesized are bound to the receptors on the cell membrane, The receptors with the ligands cluster forming the coated pitsFive steps are involved in exocytosis Vesicle trafficking edit Certain vesicletrafficking steps require the transportation of a vesicle over a moderately small distanceEndocytosis vs exocytosis This lecture explains about the differences between exocytosis and endocytosis Endocytosis is the process of capturing a substan
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/golgi_exocytosis-5ae36c743de4230037581736.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples



3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Ppt Download




Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/glucagon_glycogen_glucose-5ae36ebc8023b90036236782.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples



Exocytosis Stock Illustrations Exocytosis Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Temporal And Spatial Coordination Of Exocytosis And Endocytosis Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology




Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Reconstitution Of Calcium Mediated Exocytosis Of Dense Core Vesicles



Biphasic Exocytosis Of Herpesvirus From Hippocampal Neurons And Mechanistic Implication To Membrane Fusion Cell Discovery




Cell Calcium Pumps Britannica




Exocytosis Wikipedia
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pinocytosis-594d611e5f9b58f0fc2c5b8f.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples



17 4 Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology Libretexts
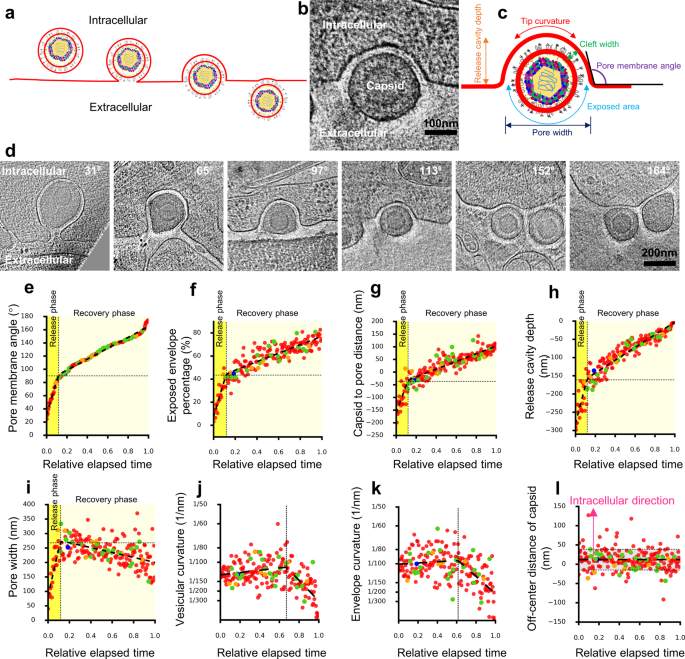



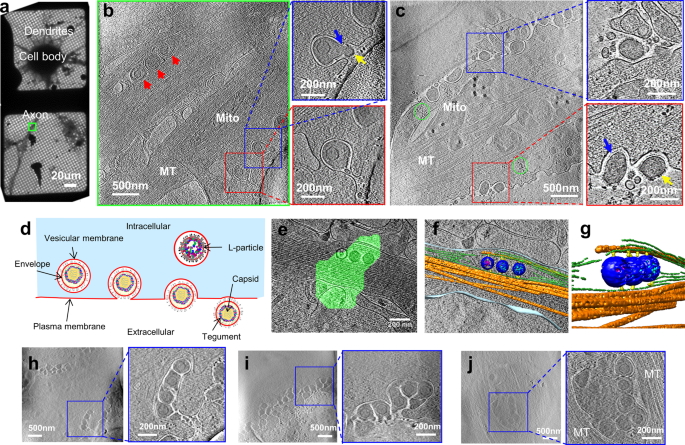
Biphasic Exocytosis Of Herpesvirus From Hippocampal Neurons And Mechanistic Implication To Membrane Fusion Cell Discovery



2 17 Exocytosis And Endocytosis Biology Libretexts
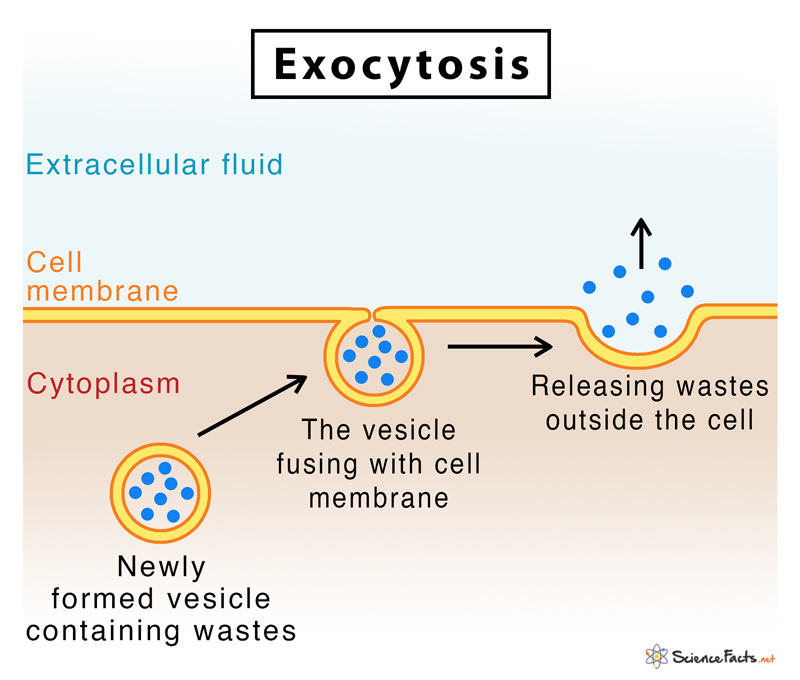



Exocytosis Definition Functions With Examples Diagram




Exocytosis Examples Triggers What Is Exocytosis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
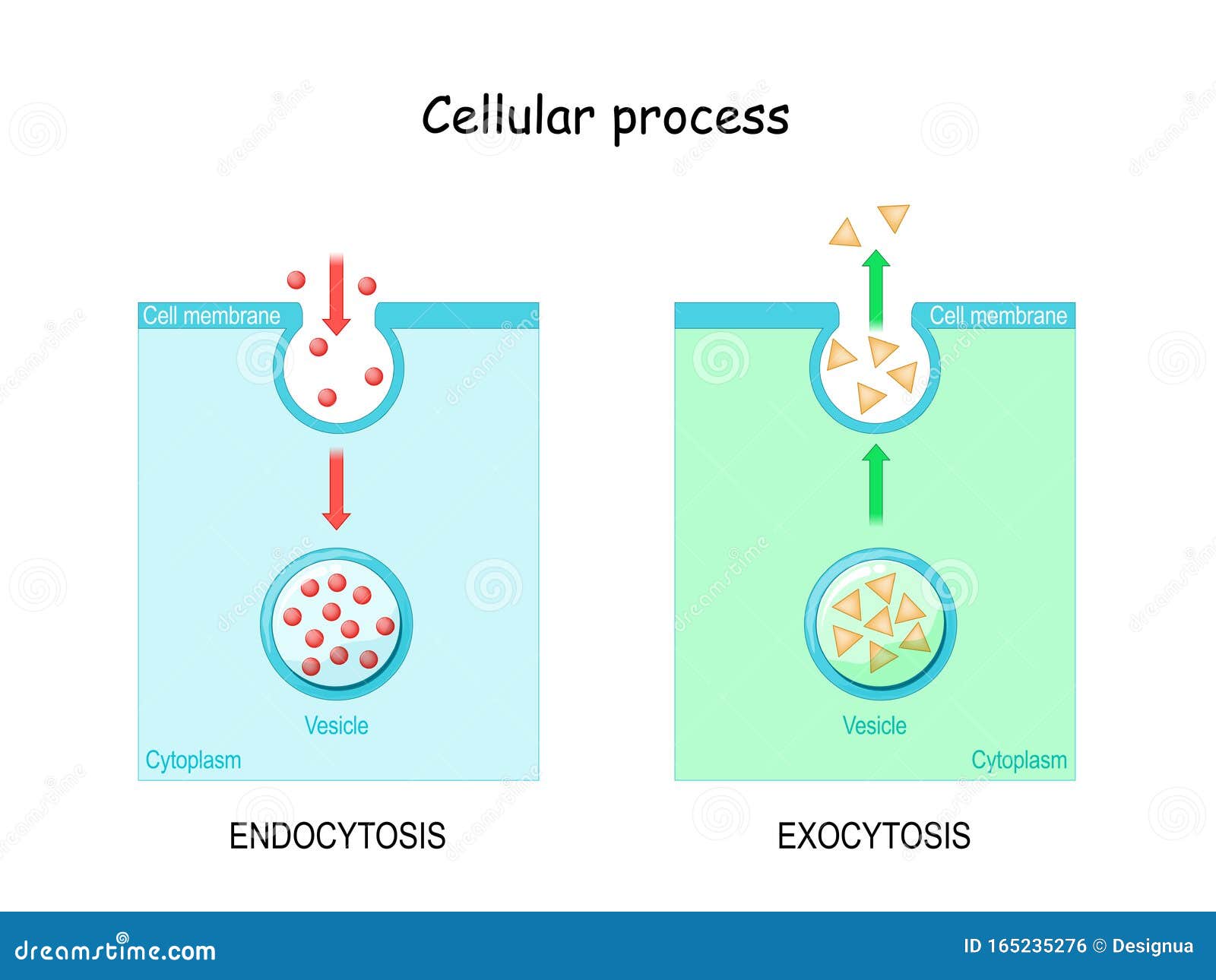



Endocytosis Stock Illustrations 85 Endocytosis Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
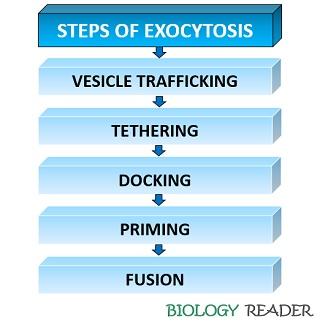



What Is Exocytosis Definition Pathways Steps Example Biology Reader
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_process-5ae370b4a9d4f900373c9b48.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples




Uh Endocytosis And Exocytosis Plasma Membrane 78 Steps Health




Learn About Diagram Of Exocytosis Chegg Com




Endocytosis Powerpoint Template Slidemodel
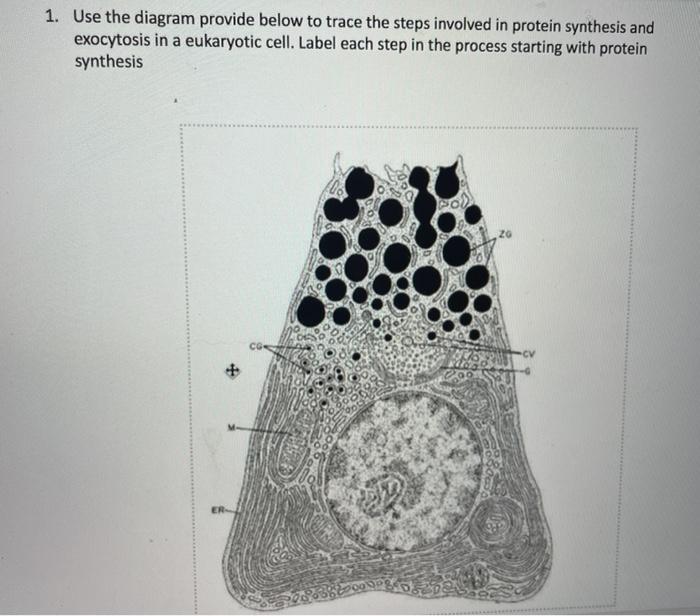



Solved 1 Use The Diagram Provide Below To Trace The Steps Chegg Com




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks




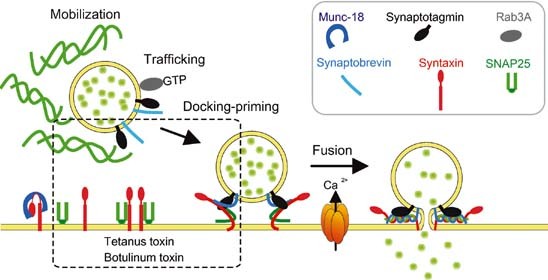
Ca2 Regulated Exocytosis And Snare Function Trends In Endocrinology Metabolism




Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Active Transport Biology I



4 Main Steps Of The Exocytosis Process Figure Adapted From An Download Scientific Diagram




Exocytosis Endocytosis Receptor Mediated Endocytosis Vesicle Transport In




What Is Membrane Trafficking Mbinfo




At The Intersection Of Exocytosis And Endocytosis In Plants Zhang 19 New Phytologist Wiley Online Library
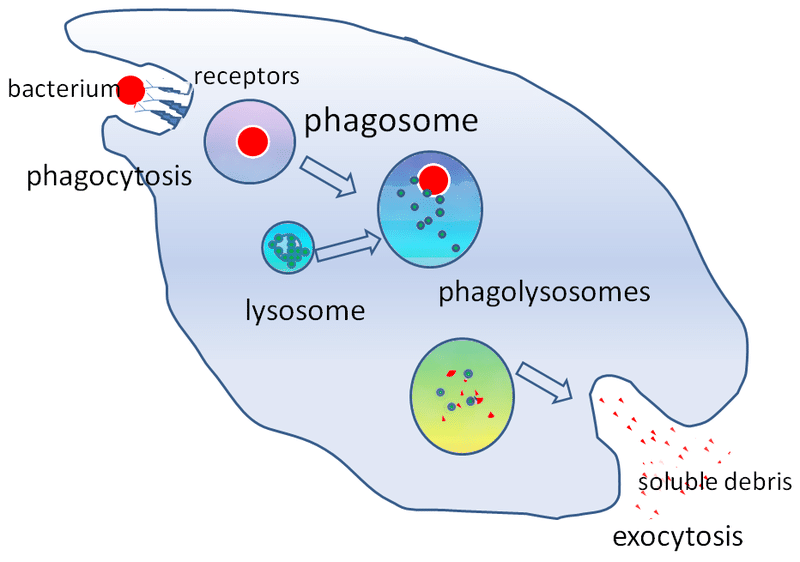



Phagocytosis Phagocytic Cells Teachmephysiology
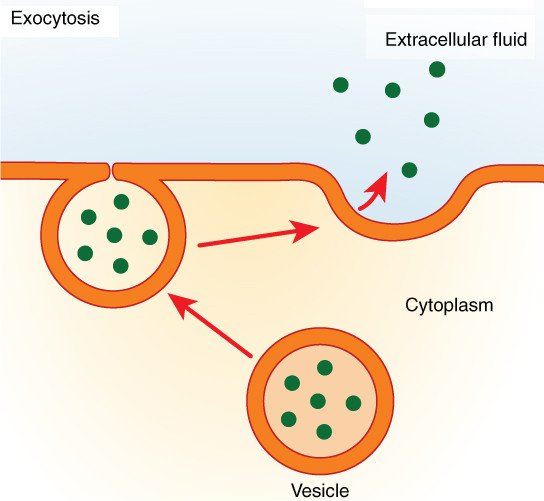



What Is Exocytosis Science Abc
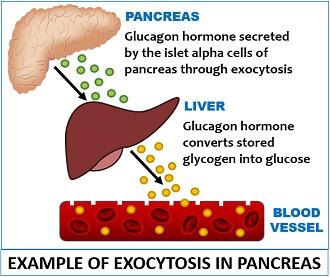



What Is Exocytosis Definition Pathways Steps Example Biology Reader




Model Of Regulated Exocytosis Key Components Involved In Docking Download Scientific Diagram
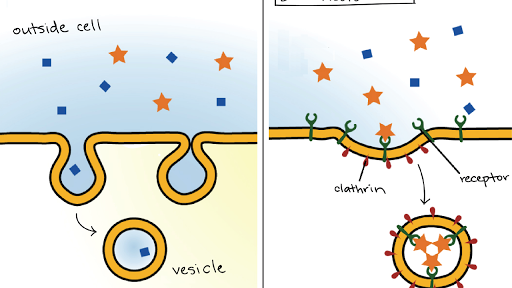



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy
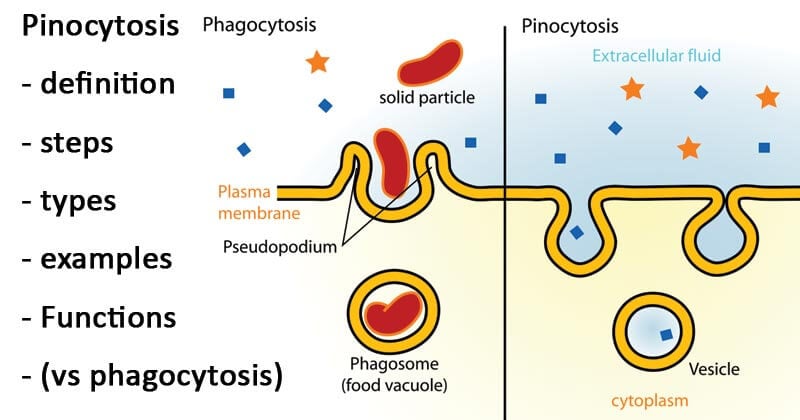



Pinocytosis Definition Steps Types Examples Vs Phagocytosis
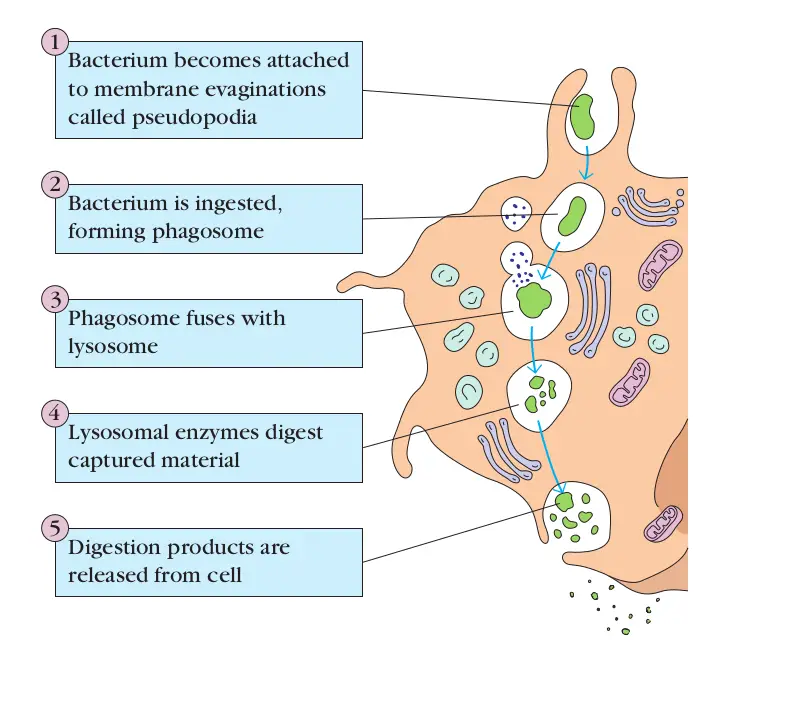



Phagocytosis Mechanism And Steps Microbe Online




Schematic Representation Of The Main Sequential Stages Of A Vesicular Download Scientific Diagram




Active Transport The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




What Is Exocytosis Definition Pathways Steps Example Biology Reader




Endocytosis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




36 Exocytosis Illustrations Clip Art Istock




Exocytosis In Non Neuronal Cells Thorn 16 Journal Of Neurochemistry Wiley Online Library




5 4b Exocytosis Biology Libretexts



What Are Some Examples Of Endocytosis Quora




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I
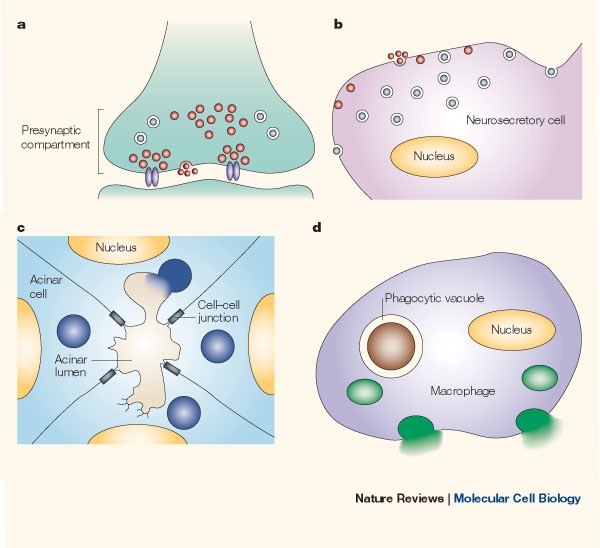



Regulated Exocytosis New Organelles For Non Secretory Purposes Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
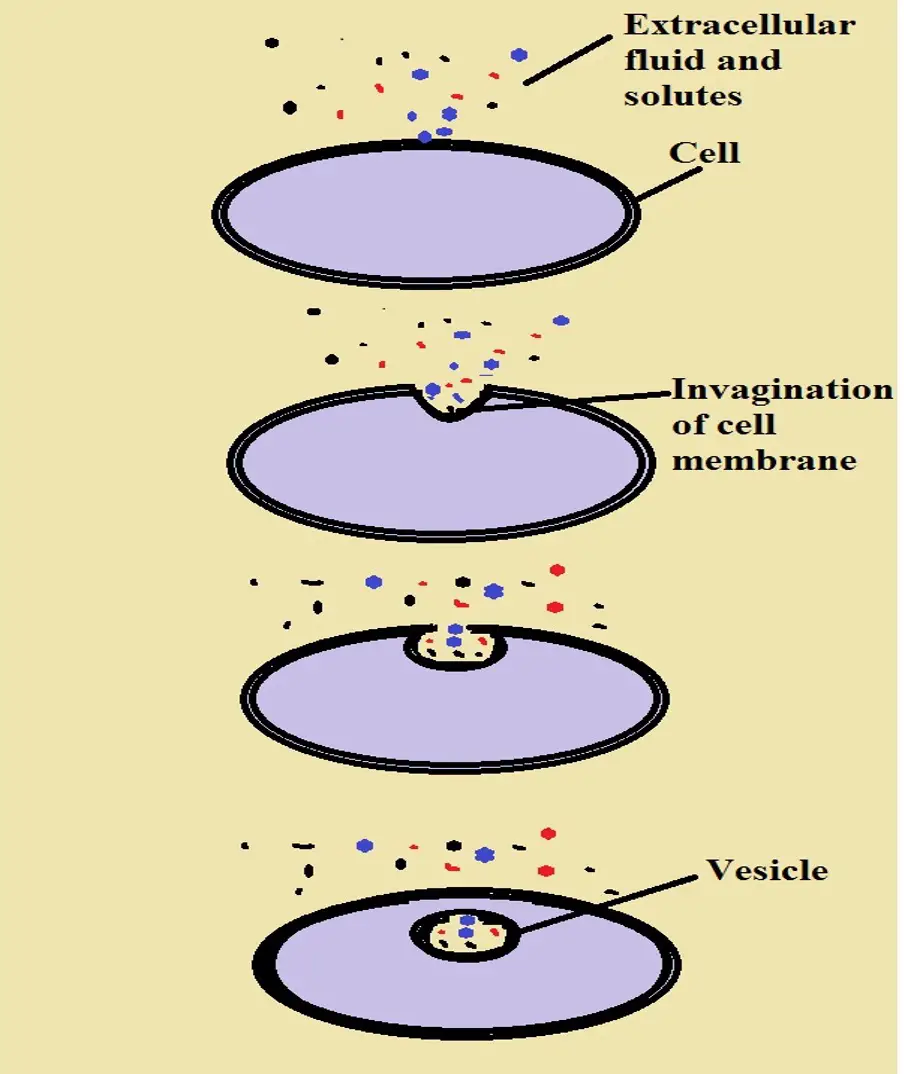



Endocytosis Definition 3 Types Active Or Passive Vs Exocytosis




Learn About Diagram Of Exocytosis Chegg Com
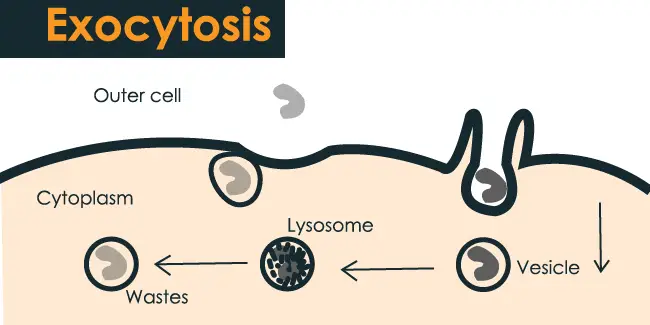



Exocytosis Definition Types Steps And Examples 6 27




Lysosomal Exocytosis And Lipid Storage Disorders Journal Of Lipid Research




Phagocytosis Neutrophil That Uses Its Plasma Membrane To Engulf A Bacterium From Endocytosis To Exocytosis Educational Scheme Digestion Process In Phagocyte Immune System Mechanism Vector Illustration Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock




Model Of The Molecular Steps Mediated Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis Download Scientific Diagram



1




Exocytosis Exo
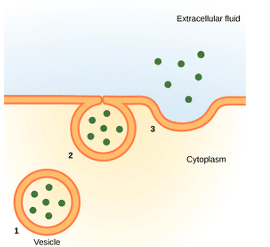



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Transport Teachmephysiology



1




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation




Neuronal Exocytosis Sciencedirect




Mono And Poly Unsaturated Phosphatidic Acid Regulate Distinct Steps Of Regulated Exocytosis In Neuroendocrine Cells Sciencedirect



Synaptic Function




Endocytosis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary



A Level Cell Biology And Transport Enzymes And Exocytosis Steemit




Stages Of Exocytosis In Secretory Cells A Formation Of Vesicles B Download Scientific Diagram




Exocytosis Ek Soh Sy Toh Sis Is The Process By Which A Cell Directs Secretory Vesicles To The Cell Membrane The Cell Biology Cell Membrane Biology Classroom




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I
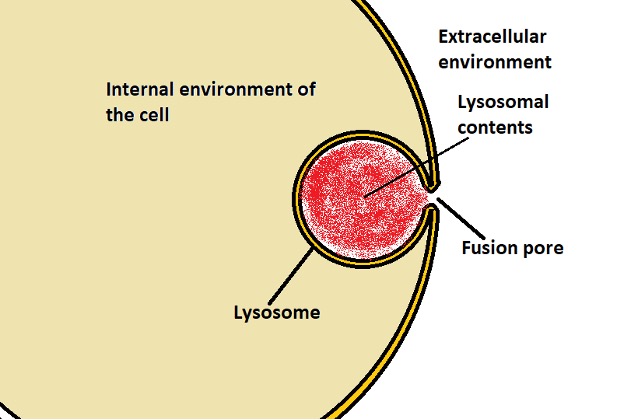



Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Definitions Types Of Exocytosis



Exocytosis Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Function Process System Blood Membrane Molecules



Endo And Exocytosis Book Chapter Iopscience



17 4 Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology Libretexts



1




Actin Remodeling In Regulated Exocytosis Toward A Mesoscopic View Trends In Cell Biology
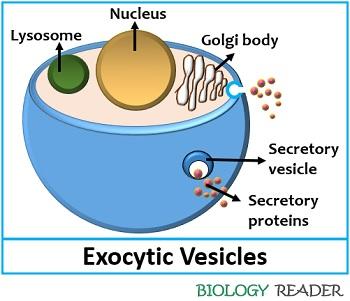



What Is Exocytosis Definition Pathways Steps Example Biology Reader
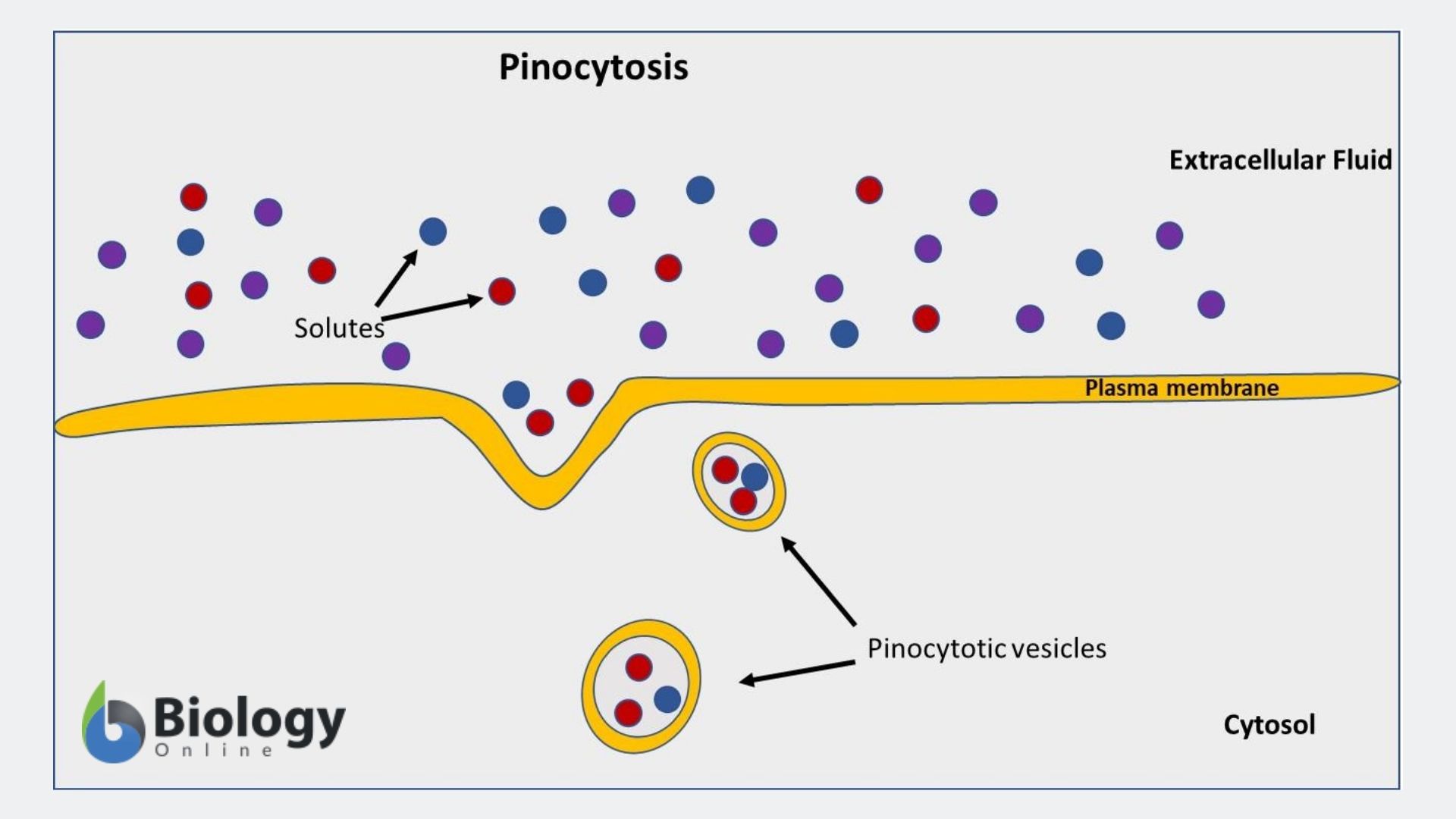



Pinocytosis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Endocytosis Exocytosis Cie A Level Biology Revision Notes



1




What Is Exocytosis Mbinfo



B 2xideauq8scm




Exorcising The Exocyst Complex Heider 12 Traffic Wiley Online Library
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis-582df6965f9b58d5b183203f.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples


